Asset Management
Strategic Asset Management Plan
Introduction
The Strategic Asset Management Plan (SAMP) provides a comprehensive framework for managing the University of Rochester's built environment, encompassing all businesses within the Facilities and Services framework. This plan aims to optimize the value derived from facilities, support sustainable growth, and enhance the university's ability to achieve its mission of education, research, patient care, and community engagement.
Objectives
The primary objectives of the SAMP are to:
- Ensure facilities management practices support the University's strategic goals in higher education and healthcare.
- Promote sustainability and minimize environmental impact.
- Identify and mitigate risks associated with facilities management.
- Continuously improve facilities management processes.
- Ensure compliance with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards.
Strategic Alignment
The SAMP aligns with the following strategic objectives:
- Educational Excellence (Meliora): Provide high-quality facilities that support teaching, learning, and research, embodying the spirit of ever better.
- Healthcare Excellence (Medicine of the Highest Order): Ensure healthcare facilities support patient care, research, and medical education, upholding the commitment to medicine of the highest order.
- Sustainability: Implement sustainable practices in the management of facilities.
- Community Engagement: Enhance the campus and healthcare environments to foster community engagement and collaboration.
- Innovation and Growth: Support the university's growth and innovation through effective facilities management.
Asset Management Framework
The asset management framework includes the following key components:
- Asset Lifecycle Management: Manage assets throughout their lifecycle, from planning and acquisition to operation, maintenance, and disposal.
- Performance Monitoring: Establish performance metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor the effectiveness of facilities management practices.
- Risk Management: Identify and mitigate risks associated with facilities management.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and improve facilities management processes.
Roles and Responsibilities
- Asset Management Committee: Oversee the implementation of the SAMP and ensure alignment with strategic objectives.
- Facilities Managers: Responsible for the day-to-day management of facilities, including planning, operation, maintenance, and disposal.
- Asset Management Department: Develop and implement asset management strategies and ensure alignment with the university's strategic objectives.
- Finance Department: Ensure financial resources are allocated effectively to support facilities management activities.
- Sustainability Office: Promote and integrate sustainable practices within facilities management.
- IT Department: Support the management of digital infrastructure related to facilities.
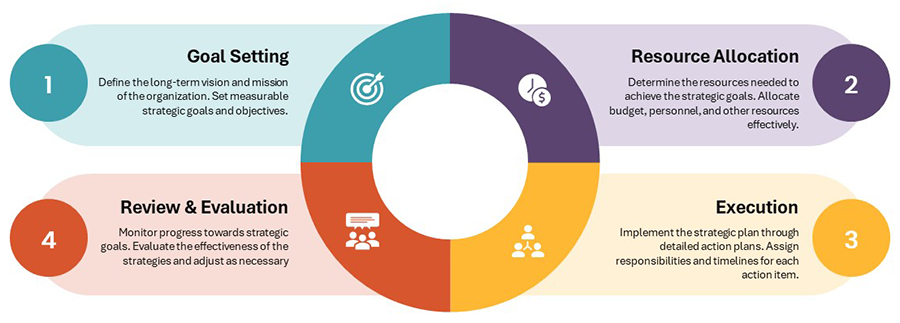
Implementation Plan
The implementation plan outlines the steps required to achieve the objectives of the SAMP:
- Assessment: Conduct a comprehensive assessment of existing facilities and identify areas for improvement.
- Planning: Develop detailed plans for the management of facilities, including maintenance schedules, upgrade plans, and sustainability initiatives.
- Execution: Implement the plans, ensuring effective management of facilities throughout their lifecycle.
- Monitoring and Review: Regularly monitor the performance of facilities management practices and review the SAMP to ensure it remains relevant and effective.
Performance Metrics and KPIs
Establish performance metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor the effectiveness of asset maintenance practices. The KPIs are divided into customer-forward metrics, working metrics, materials management metrics, safety & compliance metrics, and training metrics to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of our performance.
Customer-Forward Metrics
- Customer Satisfaction: Regular surveys and feedback to measure satisfaction with our services.
- Response Time: Track the time taken to respond to and resolve maintenance requests.
- Service Quality: Monitor the quality of maintenance work and service delivery.
- Communication Effectiveness: Evaluate how well we communicate maintenance activities and updates.
- Complaint Resolution: Measure the time and effectiveness of resolving customer complaints.
Working Metrics
- Preventive Maintenance Compliance: Percentage of scheduled preventive maintenance tasks completed on time.
- Maintenance Backlog: Volume of outstanding maintenance tasks.
- Asset Downtime: Time assets are out of service due to maintenance issues.
- Maintenance Costs: Track costs to identify opportunities for savings.
- Condition Assessment Scores: Regularly assess and score asset conditions.
- Failure Rates: Frequency of asset failures.
- Energy Efficiency: Track energy consumption related to asset performance.
- Project Turnover: Efficiency and effectiveness of project completion and turnover.
- Capital Prioritization Planning: Evaluate and prioritize capital projects.
- Risk Modeling: Identify and assess risks to develop mitigation strategies.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Analyze the total cost of owning and operating assets.
Materials Management Metrics
- Stock Levels: Monitor inventory levels to ensure optimal stock availability.
- Procurement Cycle Time: Measure the time taken to complete the procurement process.
- Supplier Performance: Evaluate suppliers based on delivery times, quality, and reliability.
- Inventory Turnover: Track how often inventory is used and replenished.
- Order Accuracy: Measure the accuracy of orders received against orders placed.
- Cost Savings: Identify cost savings achieved through efficient procurement and inventory management.
Safety & Compliance Metrics
- Incident Rate: Track the number of safety incidents and near misses.
- Compliance Audits: Measure the frequency and results of compliance audits.
- Training Completion: Percentage of staff completing mandatory safety training.
- Safety Inspections: Regular inspections to ensure compliance with safety standards.
- Corrective Actions: Track the implementation and effectiveness of corrective actions following safety incidents.
Training Metrics
- Training Participation: Measure the number of staff participating in training programs.
- Training Effectiveness: Evaluate the effectiveness of training through assessments and feedback.
- Skill Development: Track the improvement in skills and competencies post-training.
- Certification Rates: Percentage of staff obtaining relevant certifications.
- Training Hours: Total hours spent on training and development activities.
Continuous Improvement
The Asset Management Committee will regularly review the SAMP to ensure it remains relevant and effective. Feedback from stakeholders will be used to identify areas for improvement and update the plan as needed.